The Detailed Research - Part 3
As we move on from Section 2, let's delve even deeper into the research! This is Section 3.
3. Desirability and Consequences of Inequality.
Opinions on the benefits and drawbacks of inequality in society are diverse, making it a complicated and contentious issue. Here are several justifications for the favourable view of inequality, followed by some negative effects on social cohesion. We'll also provide some tactics that may be used to mitigate inequality's negative effects while maximizing its benefits.
Optimum Features of Inequality:
- Incentive for Productivity and Innovation: People may be highly motivated to work harder and more creatively to better their financial situation when faced with inequality.
- Optimum Allocation of Resources: Since inequality promotes the effective use of money and skill, some degree of inequality can be considered an efficient allocation mechanism.
- Skills and Effort Reward: Inequality may be used as a means of rewarding people for their abilities, knowledge, and hard work in a meritocratic society.
- Economic Development: Due to the fact that wealthy people frequently reinvest their income in companies and endeavors that generate employment and boost the economy, inequality can actually be a positive indicator of economic progress.
- Social Programs and Philanthropy: High-income or profit-making individuals or businesses can support social initiatives and charitable causes that benefit society as a whole.
Inequality's Negative Effects:
- Social Cohesion and Trust: Excessive inequality can damage social cohesion and trust, leading to crime, social discontent, and a decline in citizen collaboration.
- Health Inequalities: Increased wealth and economic inequality can cause differences in healthcare access, worsening the health of underprivileged populations.
- Differences in Education: Inequality may be sustained throughout generations by restricting chances for social mobility caused by unequal access to high-quality education.
- Unequal Treatment in Politics: Political inequality can result from economic disparity because wealthier people may have more sway over how laws are made.
- Destitution and Financial Volatility: Inequality-driven widespread poverty can contribute to economic instability and a shrinking customer base, both of which can hinder overall economic growth.
Methods to Reduce Adverse Effects and Utilize Advantageous Features:
- Progressive Taxation: Implement progressive tax structures that promote social programs and wealth redistribution to lessen income inequality.
- Invest in Education: To level the playing field and encourage social mobility, ensure that everyone has equal access to high-quality education.
- Labour Market Reforms: To lessen economic gaps, put laws protecting workers' rights, setting minimum pay requirements, and fostering job stability into place.
- Universal Basic Income (UBI): Consider implementing UBI as a safety net and a way to guarantee that every person has access to a minimal level of living.
- Promote Philanthropy: Encourage and provide incentives for affluent people to participate in charitable endeavours that advance society.
- Strengthen Social Safety Nets: Create extensive social safety nets that lessen poverty and offer assistance to disadvantaged groups.
- Regulate Financial Markets: Put rules in place to curb excessive financial speculation and lessen the disparity in wealth brought on by financial bubbles.
In conclusion, even if there are justifications for a certain amount of disparity, it is critical to address the detrimental effects of high inequality through social and governmental activities. Achieving a more equitable and successful society requires striking a balance between the beneficial features of inequality and attempts to reduce its negative effects. This is a difficult but necessary undertaking.
 |
| The Key Premises of Equality Impact Investing Project (EIIP), with the goal of a positive equality impacts. Source |
 |
| Health and the connectivity divide. This specific data highlights as quality health information and services become more reliant on digital technologies, it's important to see if the world is catching up as well. Source |
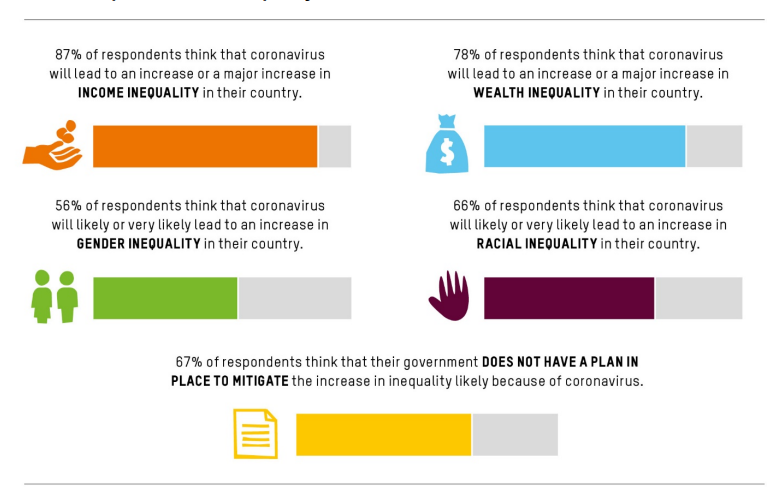
Before ending this section off, we hope that you've learnt something from this, and these graphs showcase the image well. We hope it answered the main question well, and don't forget to like and share this blogpost. See you in Section 4!
— RL




Comments
Post a Comment